Key Nutritional Needs of Seniors
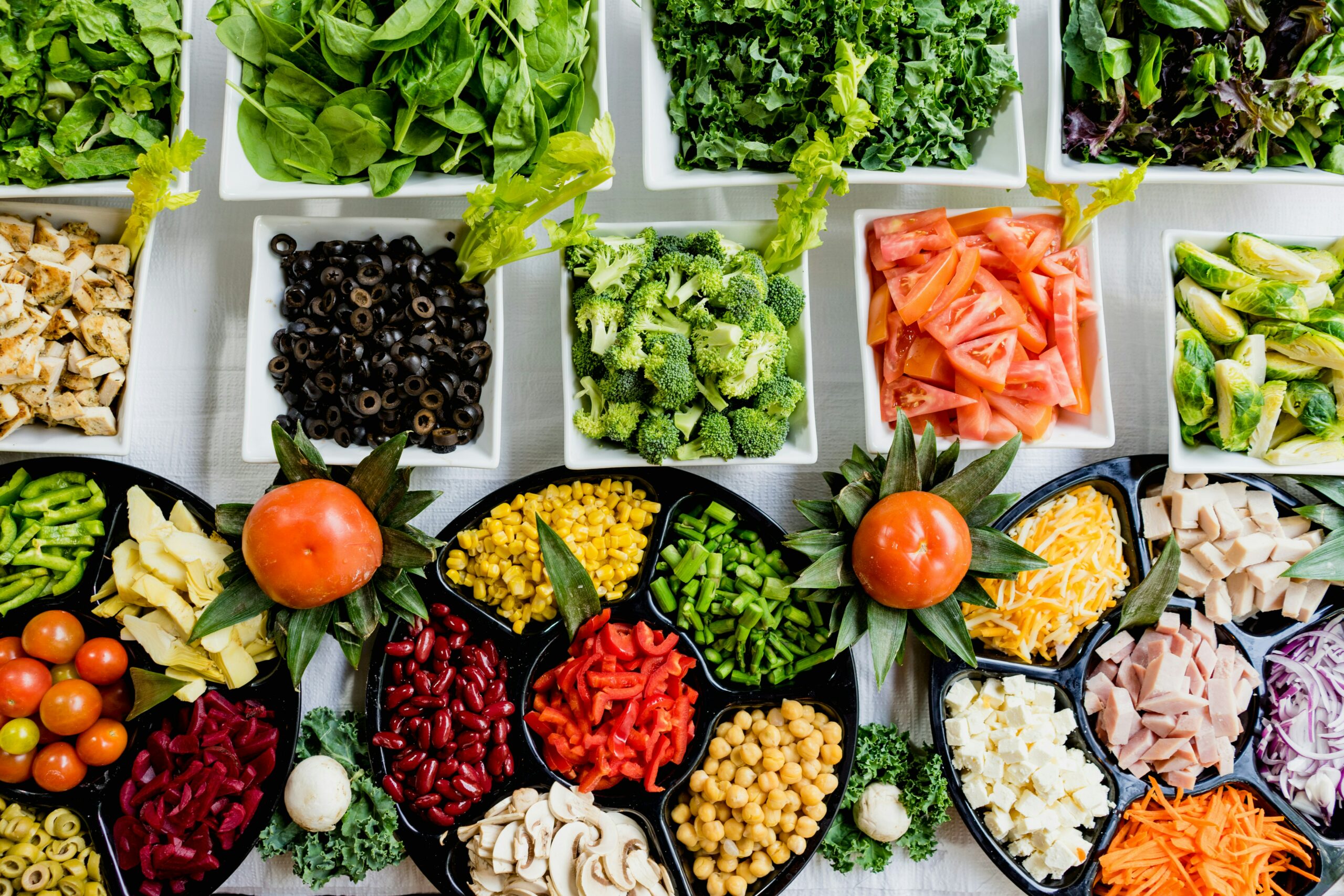
Laserbook, Laser Book: As individuals age, there are specific nutritional needs that become increasingly important for seniors to maintain good health and well-being. One key nutritional need for seniors is an adequate intake of fiber, which can help prevent constipation and promote gut health. Foods rich in fiber such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes can also help lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Another essential nutrient for seniors is vitamin D, which plays a crucial role in maintaining bone health and preventing osteoporosis. Seniors may have reduced sun exposure and decreased ability to synthesize vitamin D from sunlight, making it important to include dietary sources such as fortified milk, fatty fish, and eggs. Adequate vitamin D intake is necessary for the absorption of calcium, another vital nutrient for seniors to support bone strength and prevent fractures.
Challenges Faced by Seniors in Meeting Dietary Needs
Meeting dietary needs can be a significant challenge for seniors due to various factors. One common obstacle is a decrease in appetite and taste changes that can accompany aging. This can lead to reduced food intake and potentially missing out on essential nutrients needed for optimal health.
Limited mobility and access to grocery stores or fresh produce can also impede seniors from obtaining a diverse and balanced diet. In some cases, financial constraints may further restrict options for purchasing nutritious foods, leading to potential deficiencies in key vitamins and minerals essential for maintaining overall well-being.
Importance of Protein and Calcium for Elderly Nutrition
Calcium is a crucial mineral for elderly nutrition as it plays a vital role in maintaining strong bones and teeth. As we age, our bones tend to weaken, increasing the risk of fractures and osteoporosis. Therefore, ensuring an adequate intake of calcium through sources like dairy products, fortified foods, and leafy green vegetables is essential for seniors to support their bone health.
Protein is equally important for the elderly as it helps in preserving muscle mass, strength, and overall physical function. With age, muscle mass naturally declines, making it more challenging for seniors to perform daily activities. Including protein-rich foods such as lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy, legumes, and nuts in their diet can help seniors maintain their muscle mass and support healthy aging.
• Calcium is crucial for maintaining strong bones and teeth in the elderly
• Adequate intake of calcium can help prevent fractures and osteoporosis
• Good sources of calcium include dairy products, fortified foods, and leafy green vegetables
• Protein is important for preserving muscle mass and strength in seniors
• Including protein-rich foods like lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy, legumes, and nuts can help maintain muscle mass
• Protein also supports overall physical function in the elderly
What are the key nutritional needs of seniors?
Seniors have increased needs for protein, calcium, vitamin D, and B vitamins to support bone health, muscle strength, and overall well-being.
What are some challenges faced by seniors in meeting their dietary needs?
Some challenges faced by seniors include decreased appetite, difficulty chewing or swallowing, restricted diets due to medical conditions, and limited access to nutritious foods.
Why is protein important for elderly nutrition?
Protein is essential for maintaining muscle mass, strength, and function in seniors. It also supports immune function and wound healing.
How does calcium benefit the elderly?
Calcium is crucial for maintaining strong bones and preventing osteoporosis in seniors. It also supports heart health, nerve function, and muscle contractions.
What are good sources of protein for seniors?
Good sources of protein for seniors include lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
How can seniors ensure they are getting enough calcium in their diet?
Seniors can ensure they are getting enough calcium in their diet by consuming dairy products, fortified plant-based milks, leafy green vegetables, tofu, and almonds. They may also consider taking a calcium supplement if needed.
Are there any specific recommendations for protein and calcium intake for seniors?
The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for protein for seniors is around 0.8 grams per kilogram of body weight per day. For calcium, the RDA is 1200 mg per day for adults over 50 years old.
What should seniors do if they have trouble meeting their protein and calcium needs through diet alone?
Seniors who have trouble meeting their protein and calcium needs through diet alone may benefit from consulting a registered dietitian or healthcare provider for personalized recommendations and guidance. They may also consider incorporating protein and calcium-rich supplements or fortified foods into their diet.